DOM (Document Object Model)
What is the DOM?
The DOM (Document Object Model) is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents.
It represents the structure of a document as a tree-like hierarchy of objects. Each object represents a part of the document, such as an element, attribute, or text.
Browser Environment
When you open a webpage, the browser creates a special environment to run JavaScript. This environment includes:
- The window object: Represents the browser window or tab
- The document object: Represents the webpage content
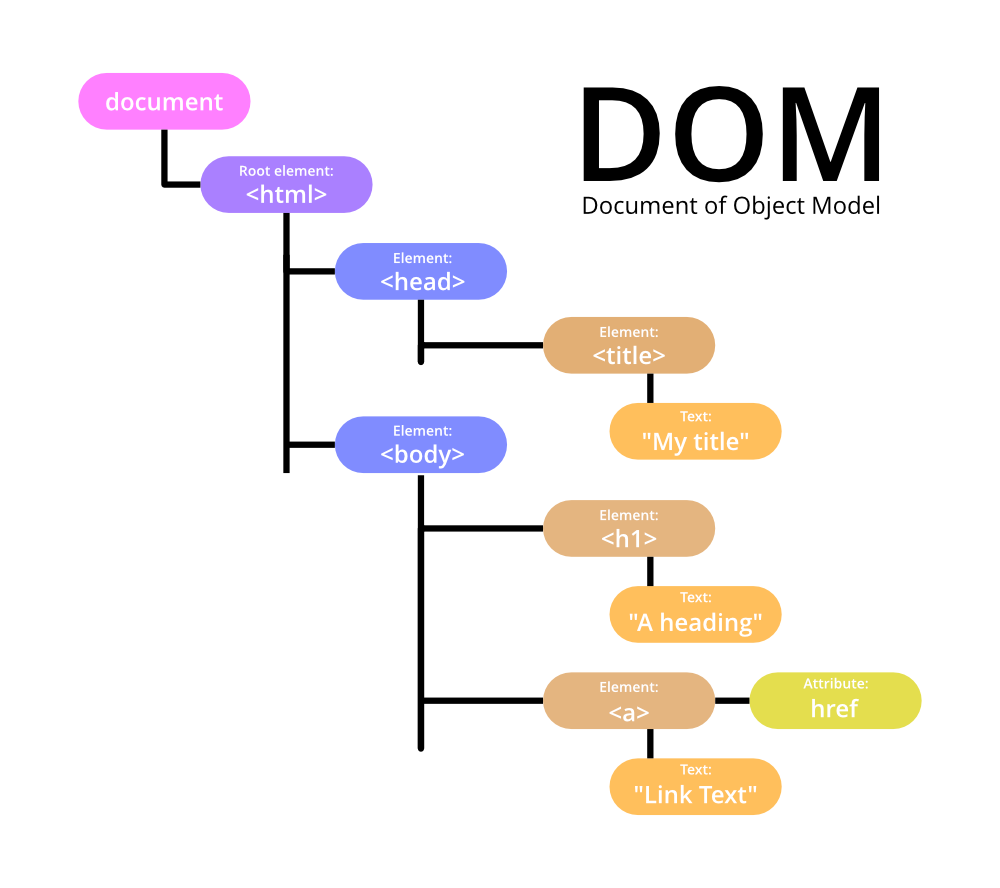
DOM Tree Structure
The DOM represents HTML as a tree-like structure of objects. Each HTML tag becomes an object, nested tags become child objects of their parent. Text within tags becomes text objects.
Imagine your HTML document as a family tree:
- The
<html>tag is the root (great-grandparent) - Tags inside
<html>(like<head>and<body>) are its children - Tags inside these are grandchildren, and so on
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome!</h1>
<p>This is my page.</p>
</body>
</html>
In this tree:
<html>is the root<head>and<body>are children of<html><title>is a child of<head><h1>and<p>are children of<body>
Traversing the DOM
You can move through the DOM tree using properties like:
- parentNode: Get the parent of an element
- childNodes: Get all child nodes of an element
- firstChild / lastChild: Get the first or last child of an element
- nextSibling / previousSibling: Get the next or previous sibling of an element
Code Examples:
Accessing Parent Node
//parentNode
//Returns the parent of the specified node in the DOM tree.
const parent = element.parentNode;
//parentElement
//Similar to parentNode, but returns null if the parent is not an element node.
const parentEl = element.parentElement;
Accessing the Child Node
//childNodes
//Returns a live NodeList of child nodes.
const childNodes = element.childNodes;
// children
// Returns a live HTMLCollection of child elements.
const children = element.children;
// firstChild and lastChild
// Return the first and last child nodes, respectively.
const firstNode = element.firstChild;
const lastNode = element.lastChild;
// firstElementChild and lastElementChild
// Return the first and last child elements, respectively.
const firstElement = element.firstElementChild;
const lastElement = element.lastElementChild;
Accessing the Sibling Node
// nextSibling and previousSibling
// Return the next and previous sibling nodes, respectively.
const nextNode = element.nextSibling;
const prevNode = element.previousSibling;
// nextElementSibling and previousElementSibling
// Return the next and previous sibling elements, respectively.
const nextElement = element.nextElementSibling;
const prevElement = element.previousElementSibling;