Introduction to Visual Hierarchy
Visual Hierarchy is a powerful technique that can help you create a better experience for your users and solve key problems with your product. It provides structure to guide users through a product, which can improve their experience and help you create well-designed interfaces.
Hierarchy is a visual design principle that designers use to show the importance of each page/screen's contents by using various features, which we'll explore in the following sections.
Elements of Visual Hierarchy
Size
Size is used to grab the attention of the user. The bigger the design element, the more it grabs attention. Size can add emphasis to a design frame or content, making it more significant.
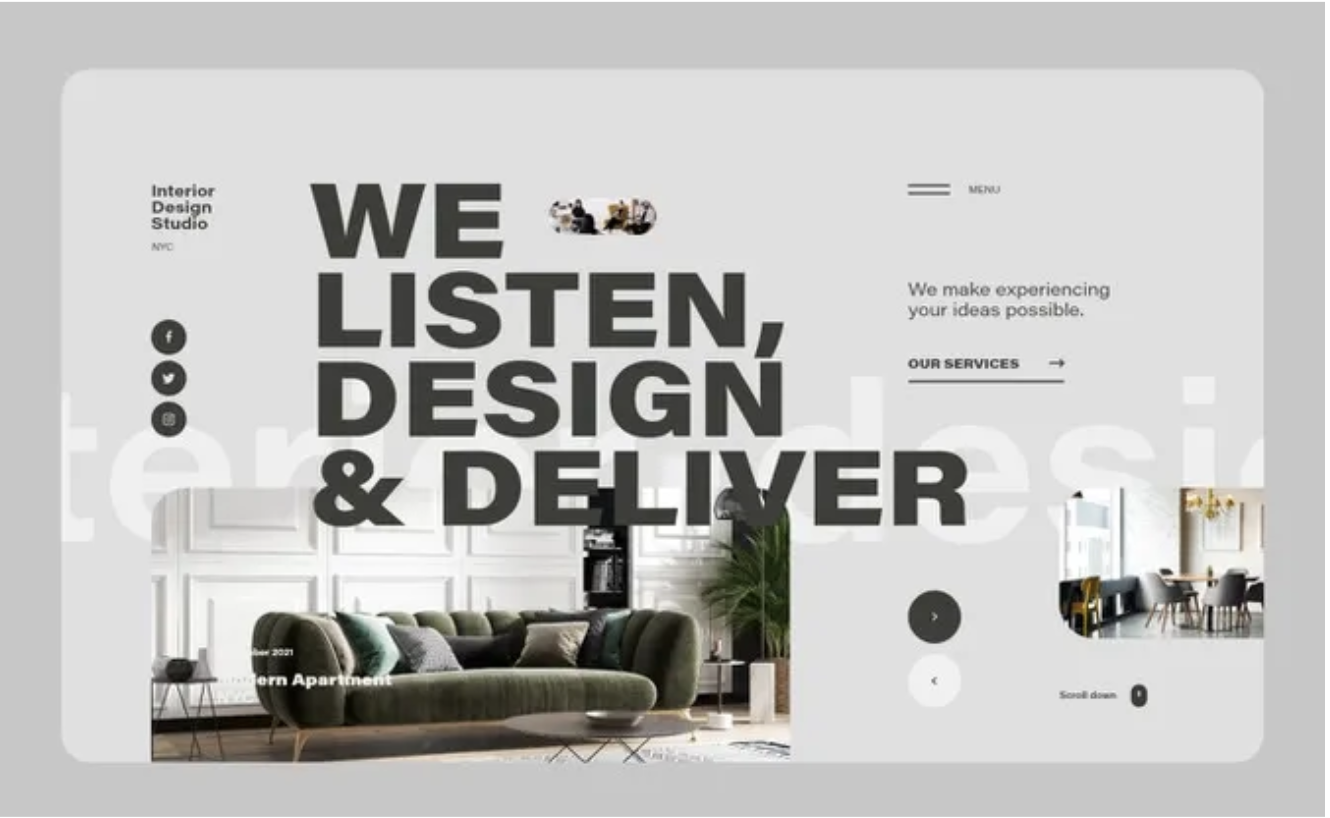
A great example of size can be found in the interior design image above. The first thing that catches your eye is the text that explains what the company does.
Color
Bright colors stand out more than muted or dull colors. Color helps set the mood for your app or website. They can reflect the personality of your brand, attract users, and better communicate your message.
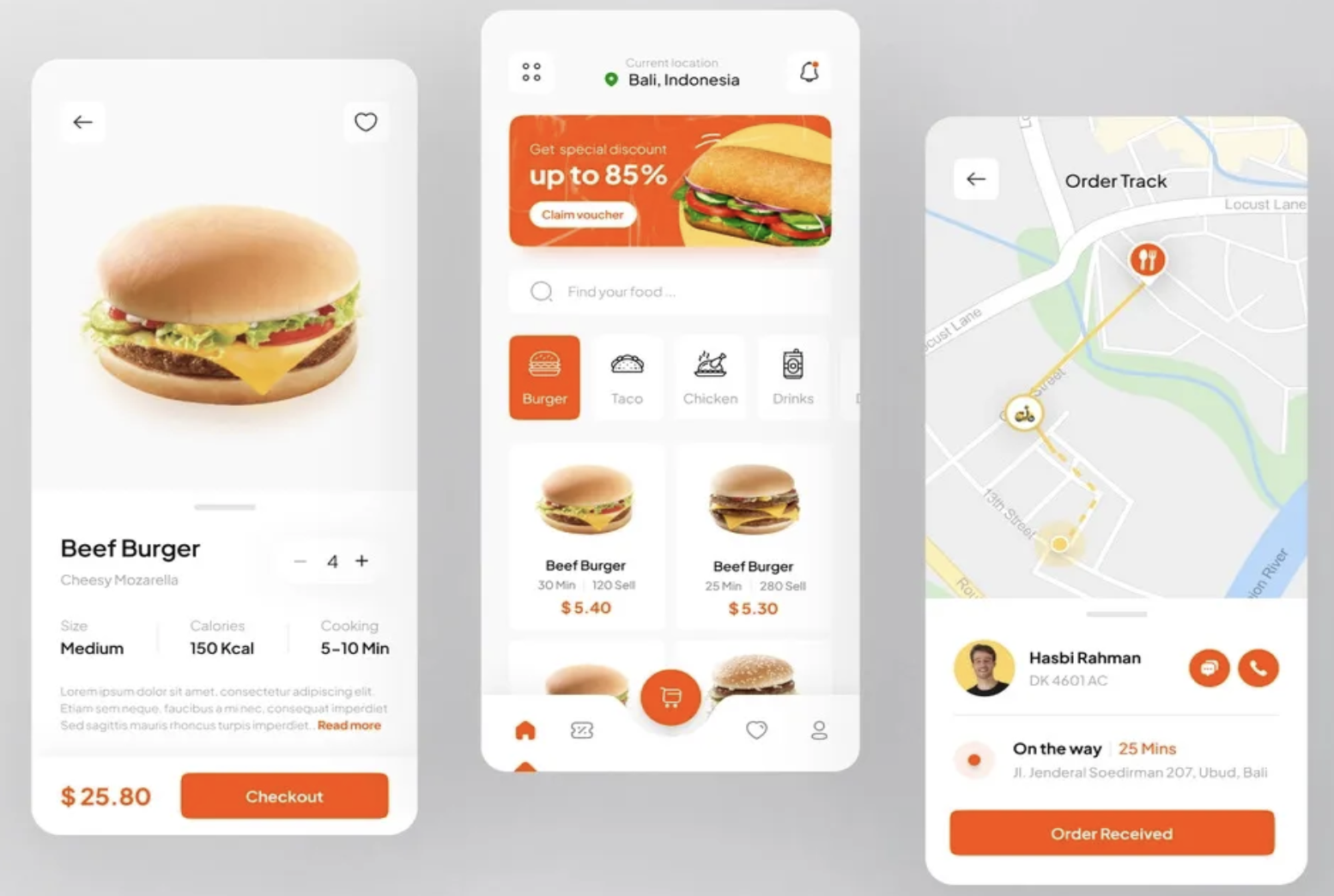
Example: The bright color above helps draw attention to the important elements on the screen. The primary color serves as a call to action. By using the primary color on buttons & text prices, users are able to anticipate how things will work and understand what action to take.
Alignment
Alignment is used to provide visual structure. Elements aligned on the same path can help them feel associated with each other, making it easier to scan. Alignment is used to form unity in design elements.
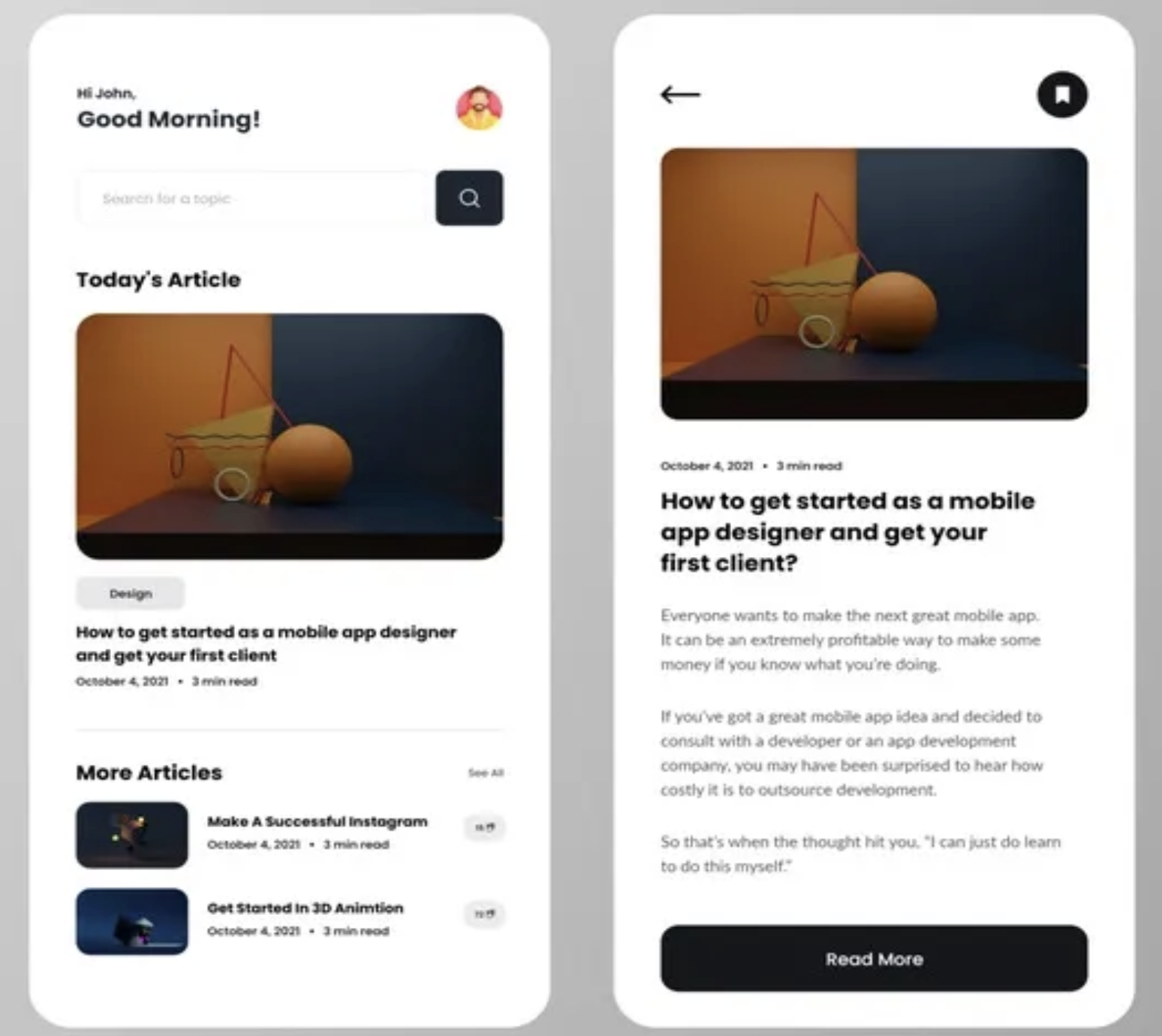
Like in the example above, the text is aligned to the left providing a better reading experience for the user. Centered text can be used for call-to-actions.
Aligning components makes the design cleaner and more structured. Alignment helps the user better understand the connections between different elements without the need for external helpers.
Repetition
Repetition is the reusing of the same or similar design elements. It is used to keep the eyes of the user familiar with the design elements of the app or website.
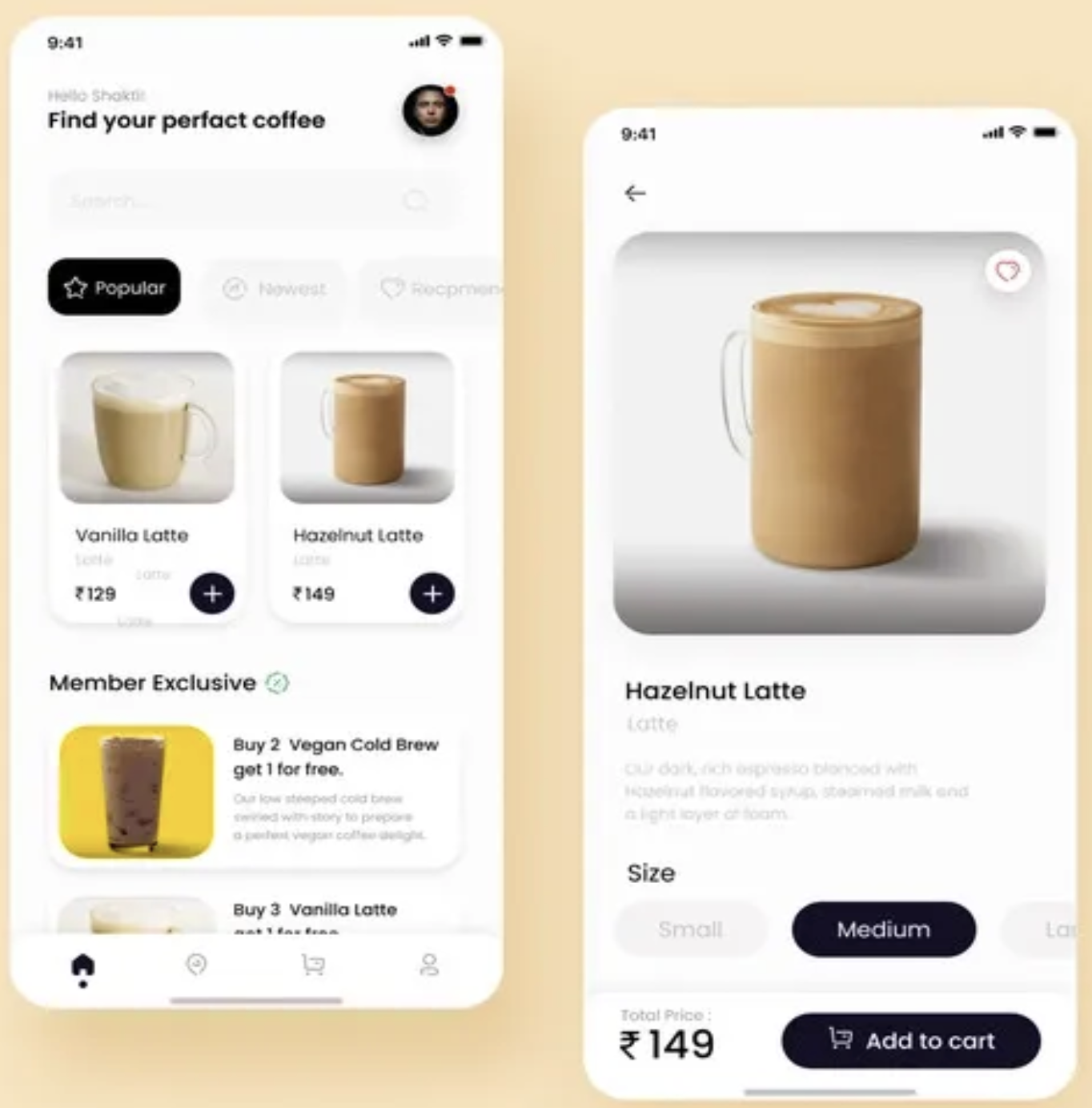
Example: Coffee ordering app
Repetition can be in many forms: Typography, Color, Size, Lines, Shapes, etc. The buttons in the design above have a dark color which makes them stand out. The Color of the button is used consistently on both screens and on different features such as the filter and the "add to cart" feature which are all call-to-action buttons. Using the same color throughout the app leads the user in a clear direction.
By using repetition we are being consistent and improving the experience for the user and making them feel comfortable as we are making users anticipate how things work.
Proximity
Proximity is the idea that similar design elements close together are perceived to be related. Elements that are placed apart mean that they belong to a separate group.

Example: Blogging App- Proximity can be determined by whitespace or color. Take the screen in the middle for example. Two elements contain blog information. The two elements are related but also they are separated by whitespace. By presenting information in scannable blocks, the user is able to scan and read the information provided to them. By using whitespace, we guide the user's eyes from one blog content to another.
White Space
White space, also known as "negative space," is empty space around the content and functional elements of a page. The basic role of white space is to let your design breathe by reducing the amount of text and functional elements that users see at once.

In the example given, whitespace is used between different UI elements, such as text, to enhance readability. Take a look at the screen on the left. Since the chair is the largest element on the page, and there is a lot of whitespace around it, it seems to be the focus of attention. An element becomes more noticeable with more negative space around it.
Essentially, the user's attention is drawn to an element with more negative space simply because there is nothing else in that area that draws their attention. Meanwhile, the right screen has elements spaced out for the user to be able to process the information easily.